
Recommended self-produced raw materials: ASO calibration raw materials: natural source, stable and reliable performance!
2025-07-28
Streptococcus pyogenes Sensitive to heat and chemical disinfectants, it often causes infections such as tonsillitis, pharyngitis, and otitis media. It is also a pathogen for pyelonephritis, puerperal fever, and scarlet fever. [1] 。
Studies have shown [2] that patients infected with Streptococcus pyogenes will produce Anti-Streptolysin O (ASO) This antibody helps in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases following streptococcal infection. Currently, routine clinical ASO detection methods include enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), immunoturbidimetry, and latex agglutination. [3] 。
Calibration material is a reference material used to calibrate measurement systems (such as analytical instruments and test kits). In the calibration function, the calibrator serves as a reference for independent variable values to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the measurement results.
ASO calibrator, by setting a known concentration of ASO standard value, is used to adjust the reaction curve of the detection reagent (such as immunoturbidimetry and ELISA reagents) to ensure that the reagent can accurately convert the detection signal (such as turbidity and absorbance) into the actual ASO concentration, avoiding deviations caused by differences in reagent batches and instrument errors.
Basic Information of ASO Calibrator
ASO Calibrator
|
|
Catalog Number:
|
LD-Ab-ASO
|
Biological Source:
|
Natural
|
Appearance:
|
Colorless or light yellow transparent liquid
|
Concentration:
|
~2000 IU/mL
|
Storage Solution:
|
1×PBS, 10% glycerol, pH 7.4
|
Storage Conditions:
|
Store at 2-8℃ for short term; store at -20℃ or below until the expiration date for long term, avoid repeated freezing and thawing.
|
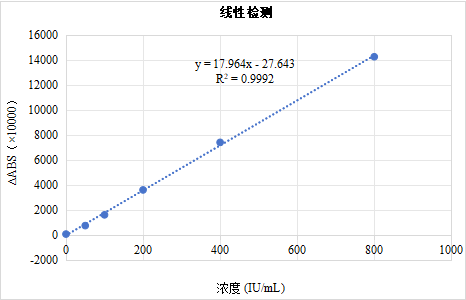
Linearity Test of ASO Calibrator
The ASO calibrator was diluted proportionally using a diluent and detected using the ASO latex reagent (Leading Medical). After fitting the curve through the origin, the correlation coefficient R>0.990, indicating good linearity.
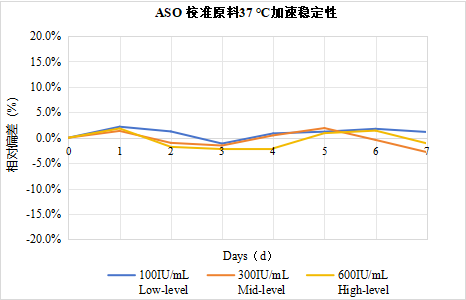
Accelerated Stability of ASO Calibrator at 37℃
The ASO calibrator was diluted to high, medium, and low concentrations using the storage buffer and placed in a 37℃ environment. At different time points, the ASO latex reagent (Leading Medical) was used for detection. The deviations of all concentrations were maintained within ±5%.
Freeze-Thaw Stability of ASO Calibrator
Under low-temperature conditions (<-20℃), the ASO calibrator was subjected to 3 freeze-thaw cycles. When detected using the ASO latex reagent (Leading Medical), the concentration deviation remained within ±5%.
Concentration (IU/mL)
|
Control
|
Repeated Freeze-Thaw 3 Cycles
|
Relative Deviation
|
480
|
485.5
|
1.10%
|
Performance Test of ASO Calibrator
The ASO calibrator was diluted to the concentrations of routine calibrators and quality control products using a diluent, and then vacuum-dried. The lyophilized ASO calibrators and quality control products were dissolved with pure water, then gradient diluted, and detected using ASO latex reagent (Leading Medical).
5.1 Test Information:
Reagent
|
LD-ASO-01
|
Analyzer
|
Hitachi 7180
|
Test Parameters
|
R1:S:R2=200:4:50
|
Wavelength (Auxiliary/Main): None/600
|
|
Reading Points: 18-34
|
|
Calibration Method: Spline
|
|
Calibration material
|
LD-CAL-ASO
|
Quality Control Product
|
LD-QC-ASO
|
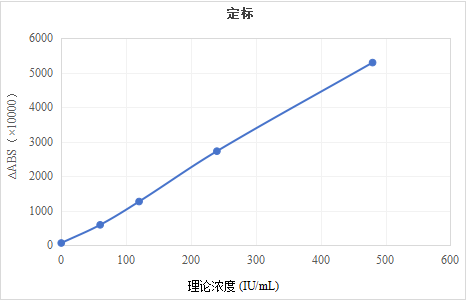
5.2 Calibration
Concentration (IU/mL)
|
∆ABS*10000
|
0
|
70.0
|
60
|
595.5
|
120
|
1269.5
|
240
|
2726.5
|
480
|
5289.0
|
5.3 Homogeneity of ASO Calibrator and Quality Control Product
n=10
|
Intra-bottle Homogeneity
|
Inter-bottle Homogeneity
|
||||
IU/mL
|
Calibration material
|
Quality Control Product 1
|
Quality Control Product 2
|
Calibration material
|
Quality Control Product 1
|
Quality Control Product 2
|
AVE
|
483.50
|
122.70
|
245.60
|
479.70
|
120.90
|
241.60
|
CV
|
0.54%
|
1.92%
|
0.69%
|
0.49%
|
1.10%
|
0.78%
|
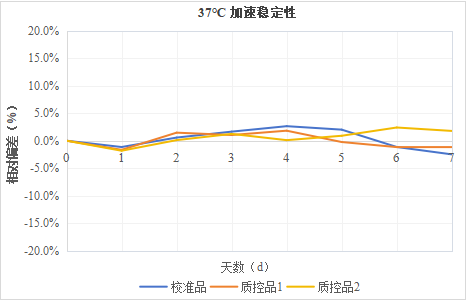
5.4 Accelerated Stability of ASO Calibrator and Quality Control Product
References
[1] Guan Xiaoshan, Liu Haiying, Zhong Huamin, et al. Incidence and clinical characteristics of invasive group B streptococcal infection in infants under one year old in Guangzhou[J]. Chinese Journal of Practical Pediatrics, 2016, 31(10): 765-768.
[2] Min Yue, Xu Qinyin, Wang Lifeng, et al. Clinical analysis of childhood rheumatic diseases and streptococcal infection[J]. Jiangsu Medicine, 2017, 43(6): 435-436.
[3] Du Min. Quantitative determination and detection analysis of anti-streptolysin O[J]. Medical Information, 2019, 32(17): 180-181.

 xy13584019024
xy13584019024